Particular properties of corrosion control
in Persian Gulf countries
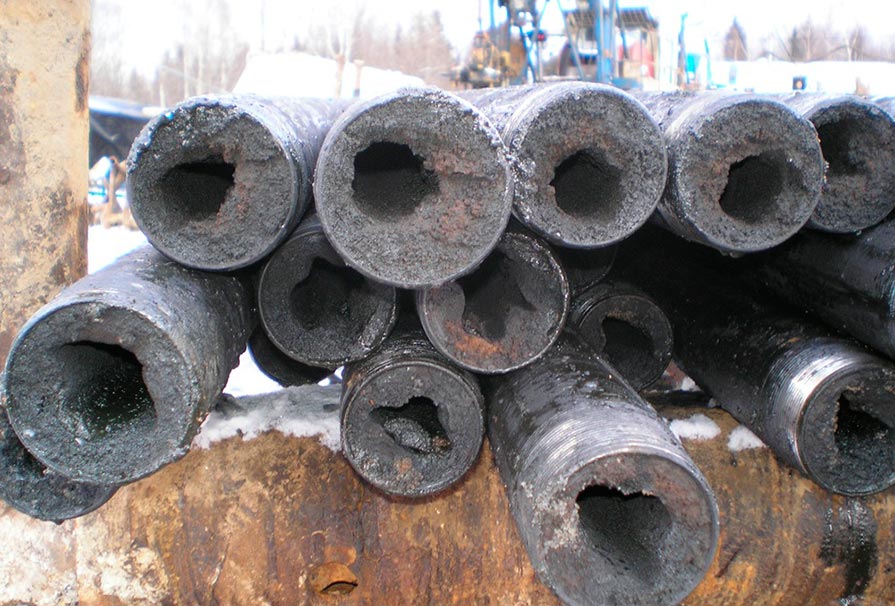
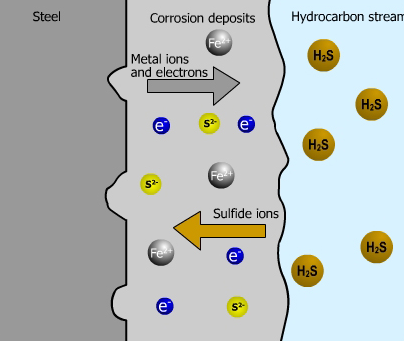
Corrosive gases СО2 and H2S in the stream of produced oil and gas condensate
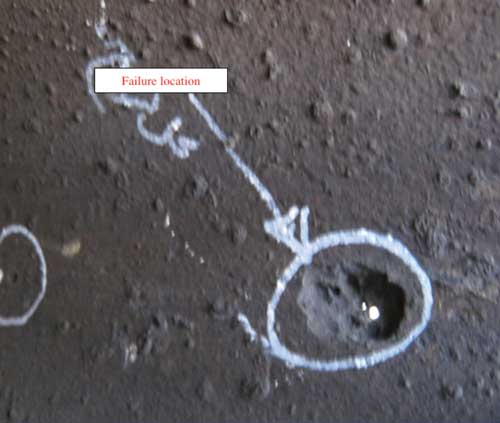
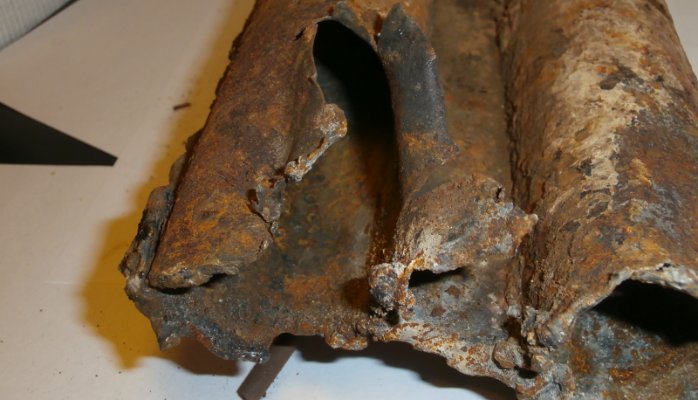
Oil and gas industry, as a rule, works in very hard conditions, such as deserts and deep sea. In such conditions, corrosion is very serious and difficult for solving problem. In desert conditions the following factors can contribute to corrosion: variation of wet and dry weather, high temperatures (about 50°C) and high humidity for the most part of the year, the salinity of the groundwater. Also, typical for this region existence of the large number of corrosive gases СО2 and H2S in the stream of produced oil, gas condensate and gas stimulate the destructive corrosion processes.
Losses from corrosion can be significantly reduced by using a number of known and effective methods. One of them, and the most simple, cheap and efficient is using corrosion inhibitors H2S and CO2.
Read more